Executive Summary
- Recent events are a strong reminder that volatility spikes are likely to continue and the need for downside protection can be effectively addressed via a low volatility strategy.
- Low volatility portfolios focus on stocks with historical price stability rather than size or growth potential, avoiding overvalued, hype-driven sectors.
- Adopting a low volatility investment approach can help achieve smoother returns and mitigate severe market downturns, offering a risk-aware alternative in today’s complex market.
A summer that was predicted to create historic growth records for global markets has instead been punctuated by disturbing turbulence. As part of the most intense global market correction since the onset of the pandemic in early-2020, the Tokyo Stock Price Index (TOPIX) suffered its steepest decline in nearly four decades (in August), whilst Wall Street’s fear gauge, the CBOE Volatility Index, experienced a historic swing before calming down.
Weak US jobs data delivered on 2nd August may have provided the spark for the market’s sell-off, while later, the unexpected rise in Japanese interest rates and yen strength continued the unwind of the Japanese yen carry trade, causing widespread unease. The large tech companies that had driven much of this year’s market rally were among the worst hit during this violent sell-off. In fact, throughout the recent earnings season, these tech giants were already struggling, as this sector failed to deliver on investors’ elevated expectations. The tech-heavy NASDAQ Composite index fell by 3.4% in the last week of July, and since its all-time high on 11th July, the NASDAQ has declined by more than 10% into the close on 5th August.
Violent volatility is here to stay
The combination of recent events serves as a strong reminder that rapid asset price swings and volatility spikes are likely to continue, especially during times when both macro risks, such as questions on the likelihood of a recession as well as how markets were caught off-guard by US economic data and geopolitical risks dominate headlines. Geopolitical risks, including the potential market impact of a Middle Eastern conflict, further contribute to market uncertainty, which is emphasised by the upcoming US presidential election on 5th November.
Fig 1: Impact of turbulent events on indices
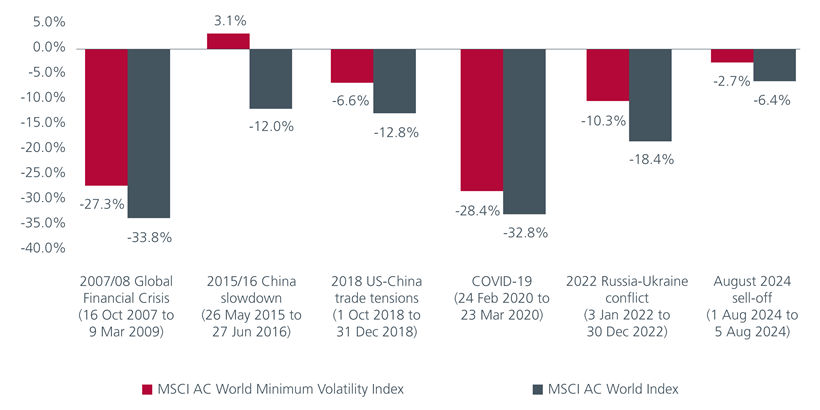
Source: Eastspring Investments, MSCI as of August 2024
Continually, the increased requirement for downside protection is also accentuated from these recent events, with such a demand being able to be fulfilled through the utility of a low volatility strategy.
Stretched valuations are a concern
As of June 2024, we were in a market where faith in future growth expectations had reached staggering levels. In Fig 2, five of the world's ten largest stocks are valued so highly that an investor would need to receive all of the company's sales revenue for over a decade with the business operating for free to break even. If you look at only earnings, the horizon of profitability stretches out even further into the future, in some cases into the 22nd century!
Some argue that these companies can grow into their valuations, but many of these companies operate in highly competitive, cyclical sectors, requiring substantial R&D investments. They are already near, or past, record sales levels, and as the largest companies in the world, doubling or tripling their revenues is no small feat.
Fig 2: Breakeven years for top ten MSCI ACWI stocks at current revenues and earnings
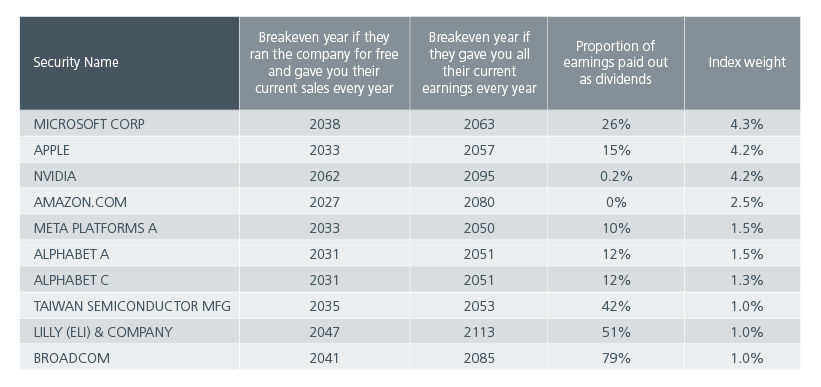
Source: MSCI as of 28 June 2024.
Although these valuations are most extreme in the technology sector, in Fig 3 you can see that other sectors have also been affected and that, compared to the past, there are more stocks above the historic median (red line) which have a higher weight in the index. This means that investors are paying higher prices for an ever-larger proportion of their portfolio.
To put it in 20th century terms they are investing during the jazz era (1920s) for a payoff at best in the rock and roll era (1950s) and in some cases in the Disco, Grunge or even early Taylor Swift era! Even this relies on two things happening until you recoup your investment:
- That the company would return you all their earnings as dividends
- That their earnings will stay the same or increase
We can see from Fig 2 that the first assumption is incorrect; in the top ten, no stock returns all their earnings and just one stock returns over half their earnings as dividends which means that the second assumption is the thing investors are pinning all their hopes on. Whilst it is true that you could also sell the stock instead of waiting for dividends, as many dotcom investors found out, you may not be able to get anything like the price you paid when you want to sell.
Fig: 3 Breakeven years for investors if they could receive all earnings
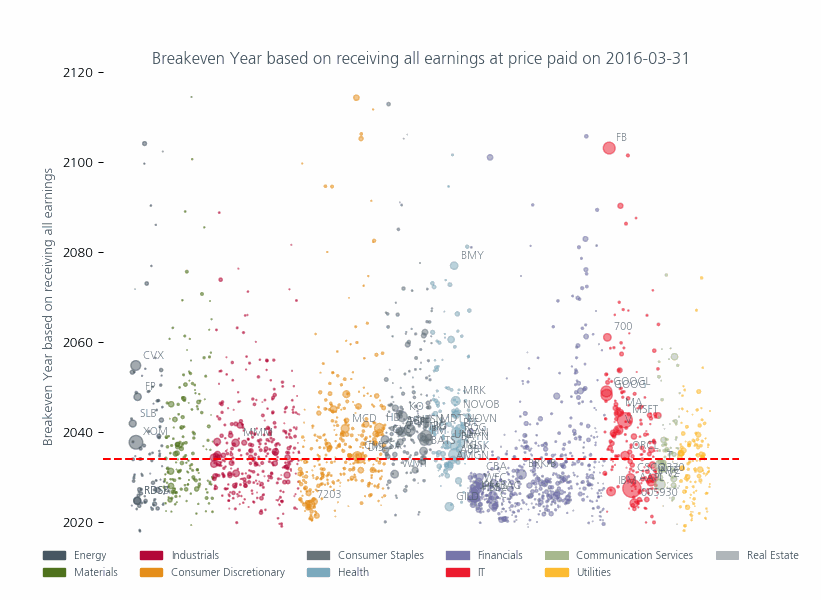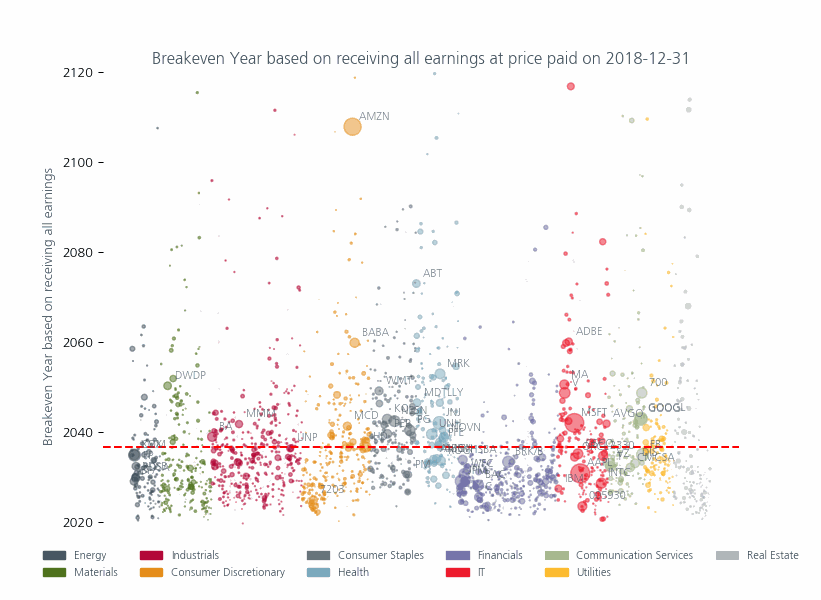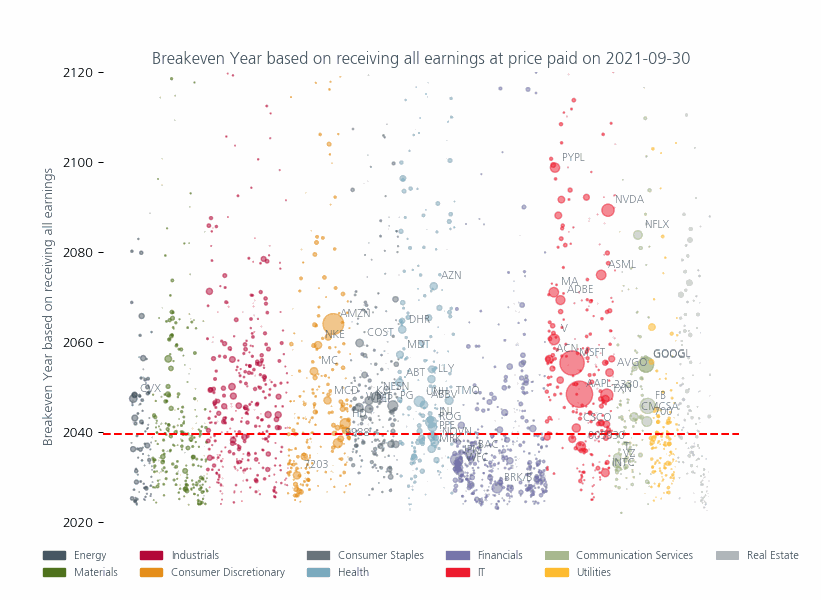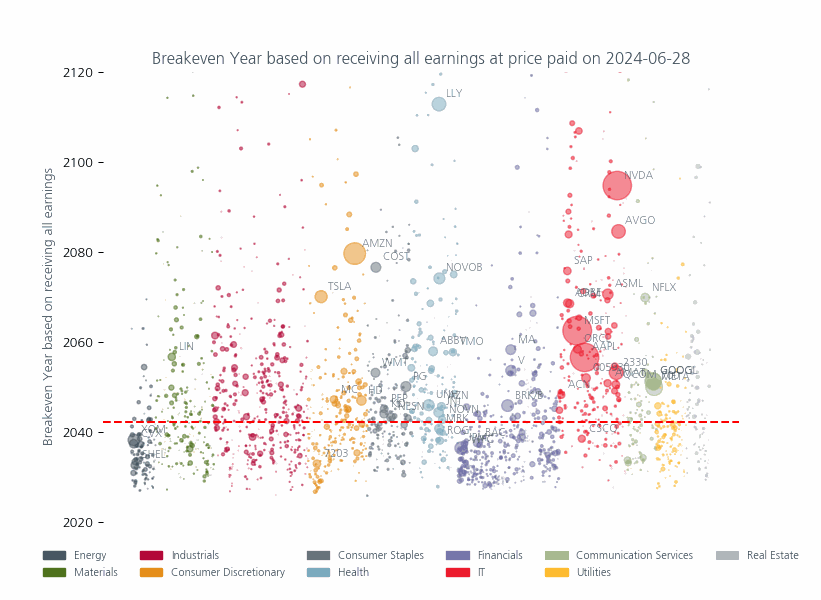
Source: MSCI Price to Earnings Ratio as of 28 June 2024. The size of circles reflect the market capitalization of the individual companies
Compounding these valuation challenges is the meteoric rise of passive investment strategies. Index funds and ETFs, which buy stocks based on their market capitalisation rather than their fundamental value, have become increasingly popular over the past two decades. While these strategies offer low-cost diversification, they have also introduced a new dynamic to the market. As more money flows into these passive vehicles, they indiscriminately purchase shares of the largest companies, regardless of their valuation or growth prospects.
This "buy regardless of price" approach has exacerbated the problem of overvaluation, particularly for the largest stocks in the market. It creates a self-reinforcing cycle where the most valuable companies continue to attract more investment simply by virtue of their size, potentially indiscriminately inflating their valuations beyond what traditional metrics would justify. This trend has contributed to the concentration of market value in a handful of mega-cap stocks, further distorting the overall market picture and potentially increasing systemic risks.
Is low volatility an antidote to the extremes?
Unlike market cap-weighted strategies, low volatility portfolios are constructed based on the historical price stability of stocks, not their size or perceived growth potential. This methodology inherently steers investors away from overvalued, hype-driven sectors and towards more fairly valued, stable companies. Low volatility strategies tend to concentrate in sectors that are often overlooked in the current growth-obsessed market, such as utilities, consumer staples, and healthcare. These sectors typically offer more consistent earnings and dividends, providing a counterbalance to the speculative fervour seen in high-flying tech stocks. Moreover, the low volatility approach’s natural aversion to market manias can serve as a safeguard against the irrational exuberance that often leads to bubble formations.
If we do the same comparison of the top ten names in the MSCI ACWI index (Fig 2) with the MSCI ACWI Minimum Volatility Index (Fig 4) you can see that the breakeven years are much earlier, and the individual weights are lower, showing a more balanced and less expensive portfolio overall.
Fig 4: Breakeven years of the top ten holdings of the MSCI ACWI Minimum Volatility Index
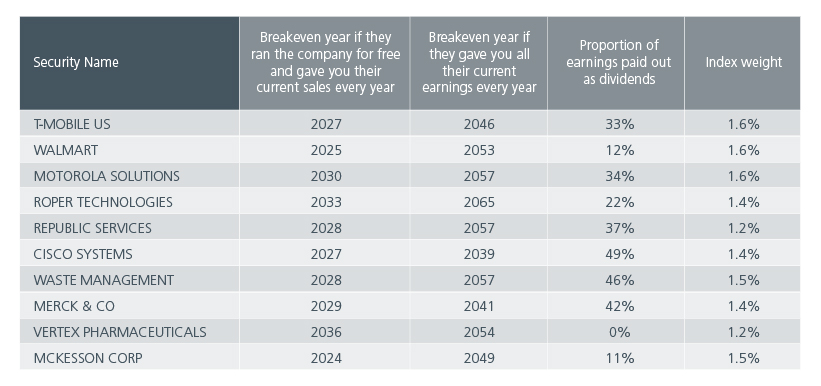
Source: MSCI as of 28 June 2024
Is it really different this time?
We can observe that the financial landscape has shifted dramatically. From blue-chip stocks to high-risk tech startups, and from traditional equities and bonds to alternative investments like cryptocurrencies, from dividend-focused stocks to growth-at-all-costs companies, the way investors perceive and measure value continues to evolve.
As investors navigate this new terrain, it is crucial to balance the allure of potential growth with the reality of tangible returns. That is not to say that AI or the weight loss drug innovations are not revolutionary, but, as we learned in the dot com bubble, you can be right about a technological change but still be wrong about which companies will profit from it or how much you should pay for them. While the stock market may not return to its dividend-focused past, pendulums rarely swing only in one direction.
In light of these market distortions, moving some assets to a low volatility investment approach can provide investors a useful alternative. By focusing on stocks with lower price fluctuations, investors can potentially achieve smoother returns over time, reducing the impact of severe market downturns. In an era where passive strategies inadvertently amplify market inefficiencies, a low volatility approach offers a thoughtful, risk-aware alternative that may be better suited to navigate the complexities of today’s financial landscape.
The information and views expressed herein do not constitute an offer or solicitation to deal in shares of any securities or financial instruments and it is not intended for distribution or use by anyone or entity located in any jurisdiction where such distribution would be unlawful or prohibited. The information does not constitute investment advice or an offer to provide investment advisory or investment management service or the solicitation of an offer to provide investment advisory or investment management services in any jurisdiction in which an offer or solicitation would be unlawful under the securities laws of that jurisdiction.
Past performance and the predictions, projections, or forecasts on the economy, securities markets or the economic trends of the markets are not necessarily indicative of the future or likely performance of Eastspring Investments or any of the strategies managed by Eastspring Investments. An investment is subject to investment risks, including the possible loss of the principal amount invested. Where an investment is denominated in another currency, exchange rates may have an adverse effect on the value price or income of that investment. Furthermore, exposure to a single country market, specific portfolio composition or management techniques may potentially increase volatility.
Any securities mentioned are included for illustration purposes only. It should not be considered a recommendation to purchase or sell such securities. There is no assurance that any security discussed herein will remain in the portfolio at the time you receive this document or that security sold has not been repurchased.
The information provided herein is believed to be reliable at time of publication and based on matters as they exist as of the date of preparation of this report and not as of any future date. Eastspring Investments undertakes no (and disclaims any) obligation to update, modify or amend this document or to otherwise notify you in the event that any matter stated in the materials, or any opinion, projection, forecast or estimate set forth in the document, changes or subsequently becomes inaccurate. Eastspring Investments personnel may develop views and opinions that are not stated in the materials or that are contrary to the views and opinions stated in the materials at any time and from time to time as the result of a negative factor that comes to its attention in respect to an investment or for any other reason or for no reason. Eastspring Investments shall not and shall have no duty to notify you of any such views and opinions. This document is solely for information and does not have any regard to the specific investment objectives, financial or tax situation and the particular needs of any specific person who may receive this document.
Eastspring Investments Inc. (Eastspring US) primary activity is to provide certain marketing, sales servicing, and client support in the US on behalf of Eastspring Investment (Singapore) Limited (“Eastspring Singapore”). Eastspring Singapore is an affiliated investment management entity that is domiciled and registered under, among other regulatory bodies, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). Eastspring Singapore and Eastspring US are both registered with the US Securities and Exchange Commission as a registered investment adviser. Registration as an adviser does not imply a level of skill or training. Eastspring US seeks to identify and introduce to Eastspring Singapore potential institutional client prospects. Such prospects, once introduced, would contract directly with Eastspring Singapore for any investment management or advisory services. Additional information about Eastspring Singapore and Eastspring US is also is available on the SEC’s website at www.adviserinfo.sec. gov.
Certain information contained herein constitutes "forward-looking statements", which can be identified by the use of forward-looking terminology such as "may", "will", "should", "expect", "anticipate", "project", "estimate", "intend", "continue" or "believe" or the negatives thereof, other variations thereof or comparable terminology. Such information is based on expectations, estimates and projections (and assumptions underlying such information) and cannot be relied upon as a guarantee of future performance. Due to various risks and uncertainties, actual events or results, or the actual performance of any fund may differ materially from those reflected or contemplated in such forward-looking statements.
Eastspring Investments companies (excluding JV companies) are ultimately wholly-owned / indirect subsidiaries / associate of Prudential plc of the United Kingdom. Eastspring Investments companies (including JV’s) and Prudential plc are not affiliated in any manner with Prudential Financial, Inc., a company whose principal place of business is in the United States of America.















